Get Started with HTML
HTML means **HyperText Markup Language** and is a markup language that tells web browsers how to structure the web pages you visit.
Tags
What's HTML?
HTML means HyperText Markup Language and is a markup language that tells web browsers how to structure the web pages you visit.
What's the element structure of HTML?
What's block-level elements?
- They are elements that force the line break.
- e.g:
<p>
What's inline-elements?
- They are elements that not break lines, be within block-level elements.
- e.g:
<span>
What's empty elements?
- They are elements that not contain closing tag, an single tag using to insert/embed something in the document. These elements contain just 'Opening tag' but inside this, insert an
/before>to work. - e.g:
<img/>element embeds an image file onto a page.
What's attributes?
- Attributes contain extra information about the element that won't appear in the content. In this example, the
classattribute is an identifying name used to target the element with style information. 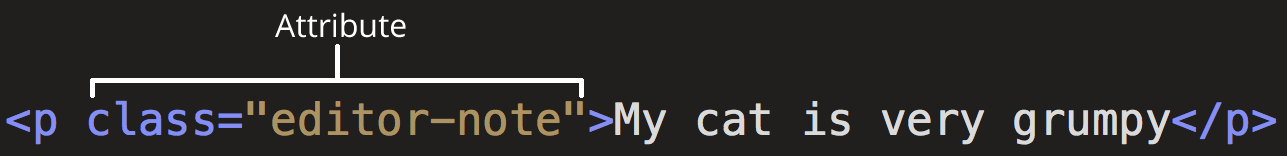
Somes attributes:
href- This attribute's value specifies the web address for the link. For example:href="https://www.mozilla.org/".title- The title attribute specifies extra information about the link, such as a description of the page that is being linked to. For example,title="The Mozilla homepage". This appears as a tooltip when a cursor hovers over the element.target- The target attribute specifies the browsing context used to display the link. For example,target="_blank"will display the link in a new tab. If you want to display the linked content in the current tab, just omit this attribute.
Boolean attributes
- Sometimes you will see attributes written without values. This is entirely acceptable. These are called Boolean attributes. Boolean attributes can only have one value, which is generally the same as the attribute name. For example, consider the disabled attribute, which you can assign to form input elements. (You use this to disable the form input elements so the user can't make entries. The disabled elements typically have a grayed-out appearance.) For example:
<input type="text" disabled="disabled" />
- As shorthand, it is acceptable to write this as follows:
<!-- using the disabled attribute prevents the end user from entering text into the input box -->
<input type="text" disabled />
<!-- text input is allowed, as it doesn't contain the disabled attribute -->
<input type="text" />
Anatomy of an HTML document
Individual HTML elements aren't very useful on their own. Next, let's examine how individual elements combine to form an entire HTML page:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en-US">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>My test page</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is my page</p>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>This is the definition used for HTML5 which is the most recent version at the time of writing this MD. It serves to define a version of HTML so that other tags work correctly, in the past this was more complex to define, but now it is enough to define this form to use HTML5 and work in any browser.<html></html>This element wraps all the content on the page. It is sometimes known as the root element.<head></head>This element acts as a container for everything you want to include on the HTML page, that isn't the content the page will show to viewers. This includes keywords and a page description that would appear in search results, CSS to style content, character set declarations, and more.<meta charset="utf-8">This element represents metadata that cannot be represented by other HTML meta-related elements, like<base>,<link>,<script>,<style>or<title>. The charset attributes sets the character set for your document toUTF-8, which includes most characters from the vast majority of human written languages. With this setting, the page can now handle any textual content it might contain. There is no reason not to set this, and it can help avoid some problems later.<title></title>This sets the title of the page, which is the title that appears in the browser tab the page is loaded in. The page title is also used to describe the page when it is bookmarked.<body></body>This contains all the content that displays on the page, including text, images, videos, games, playable audio tracks, or whatever else.
Whitespace in HTML
In the examples above, you may have noticed that a lot of whitespace is included in the code. This is optional. These two code snippets are equivalent:
<p>My name is Everton.</p>
<p>My name
is
Everton.</p>
Special characters
Special characters are not read just by typing, we need to use some code referring to this character to be able to type.
Example:
<p>In HTML, you define a paragraph using the <p> element.</p>
<p>In HTML, you define a paragraph using the <p> element.</p>
Response:
In HTML, you define a paragraph using the
element.
In HTML, you define a paragraph using the <p> element.
You can see more a bout this here -> Character Entity References Wikipedia.
HTML Comments
To comments using html, we need type <!-- text here -->.
Example:
<!-- Hello World, my name is Everton! -->
It will not affect the code, just notify who is reading the code.
